
Table of Contents
TogglePay Items Setup
This page centralizes your salary configurations and ATO compliance settings.
Financial Mapping: Set default G/L accounts for salary expenses, liabilities, and superannuation.
Tax & Compliance: Configure PAYG withholding, Medicare levies, and the 12% Superannuation Guarantee.
Payment Workflow: Link bank accounts and define journal series for seamless disbursements.
Payroll Items: Access subpages for leave accruals, earnings (base pay/overtime), and deductions.
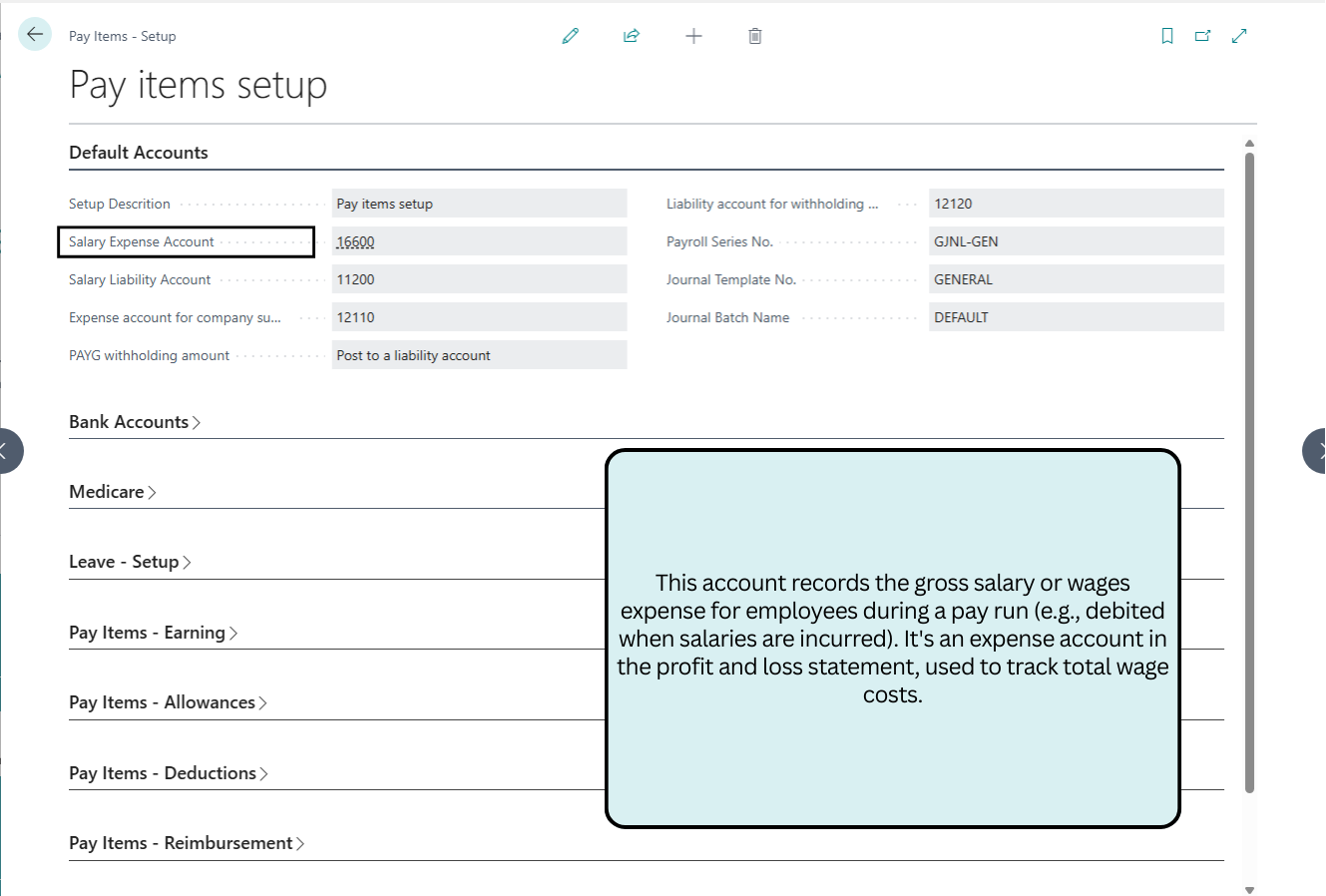
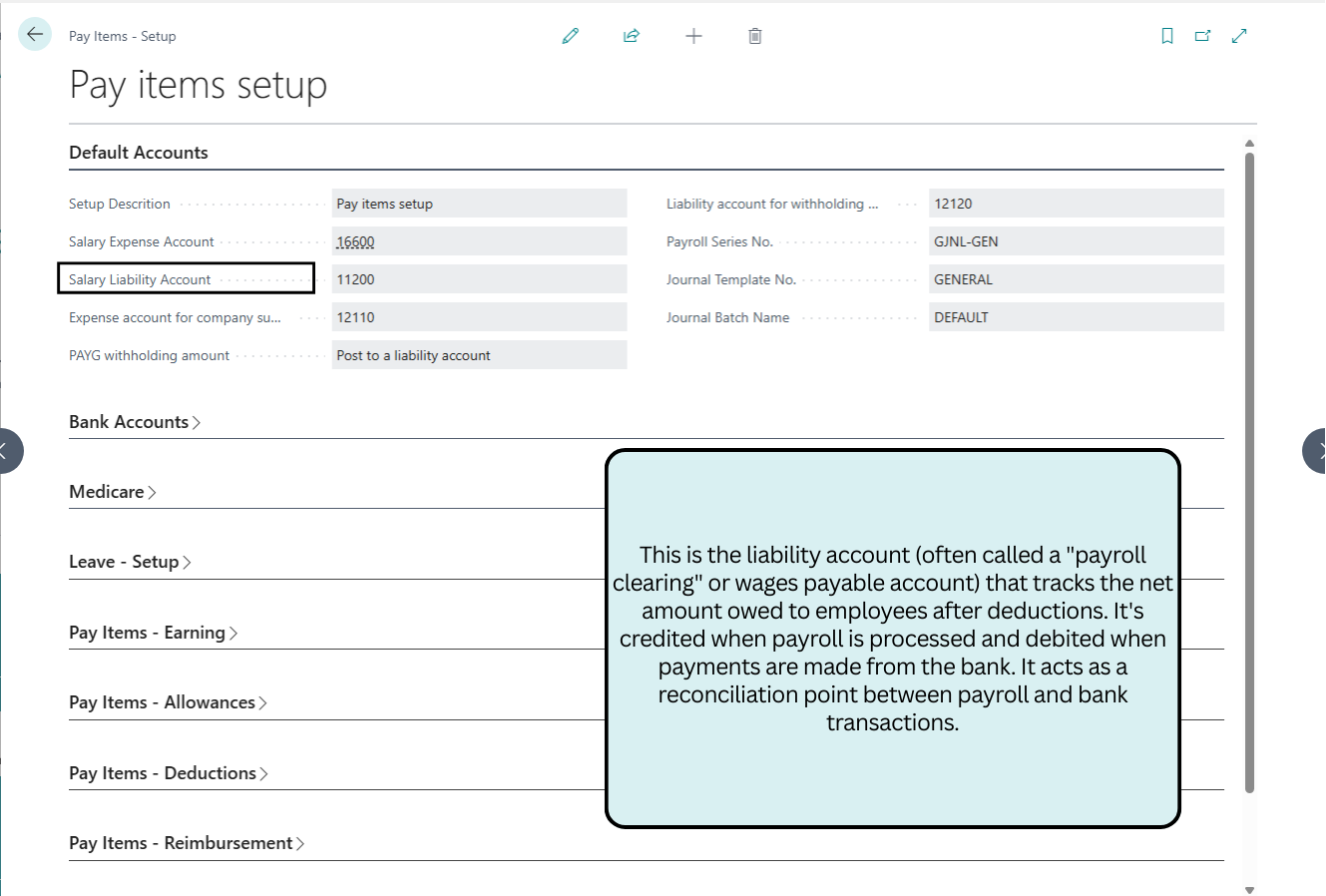
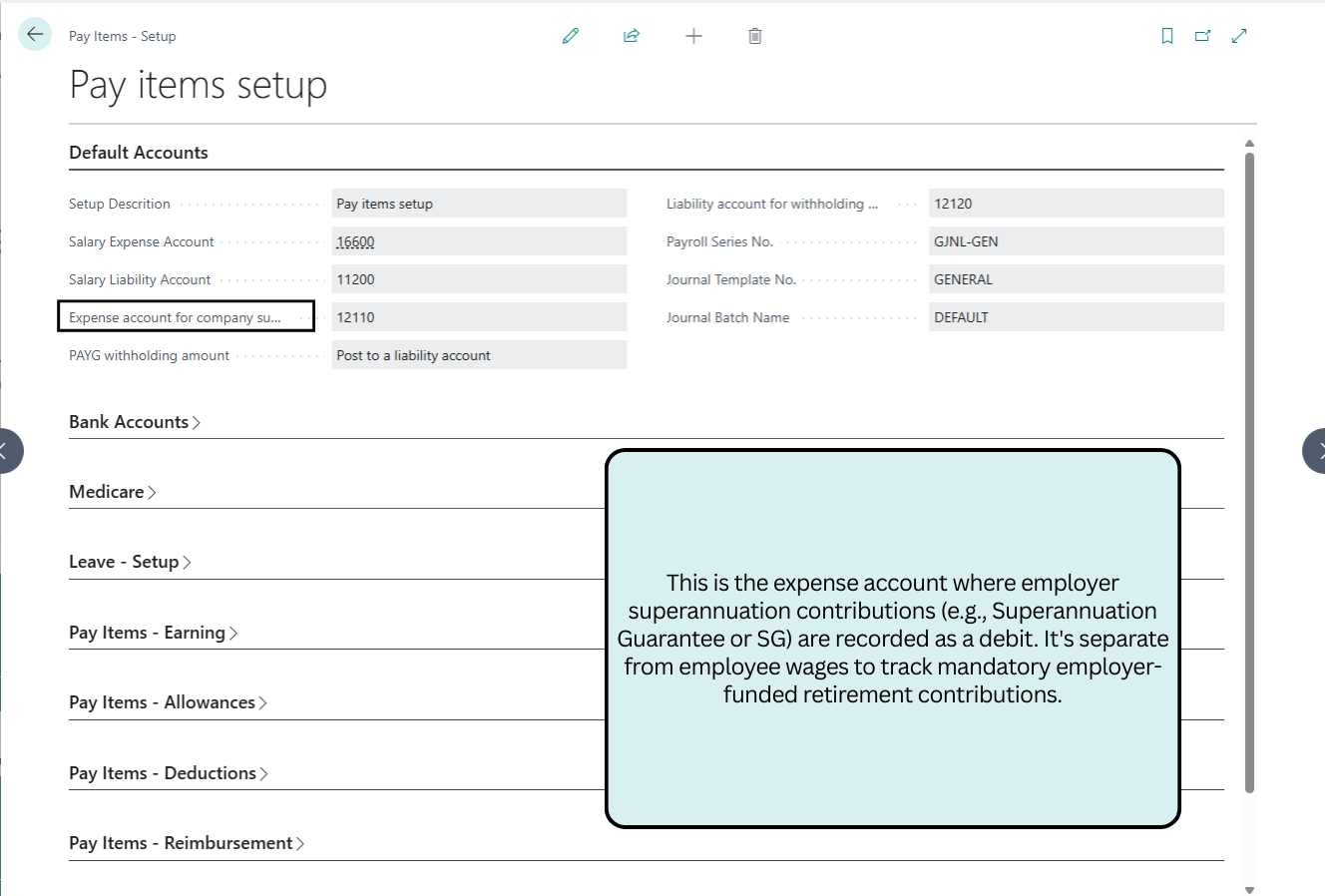
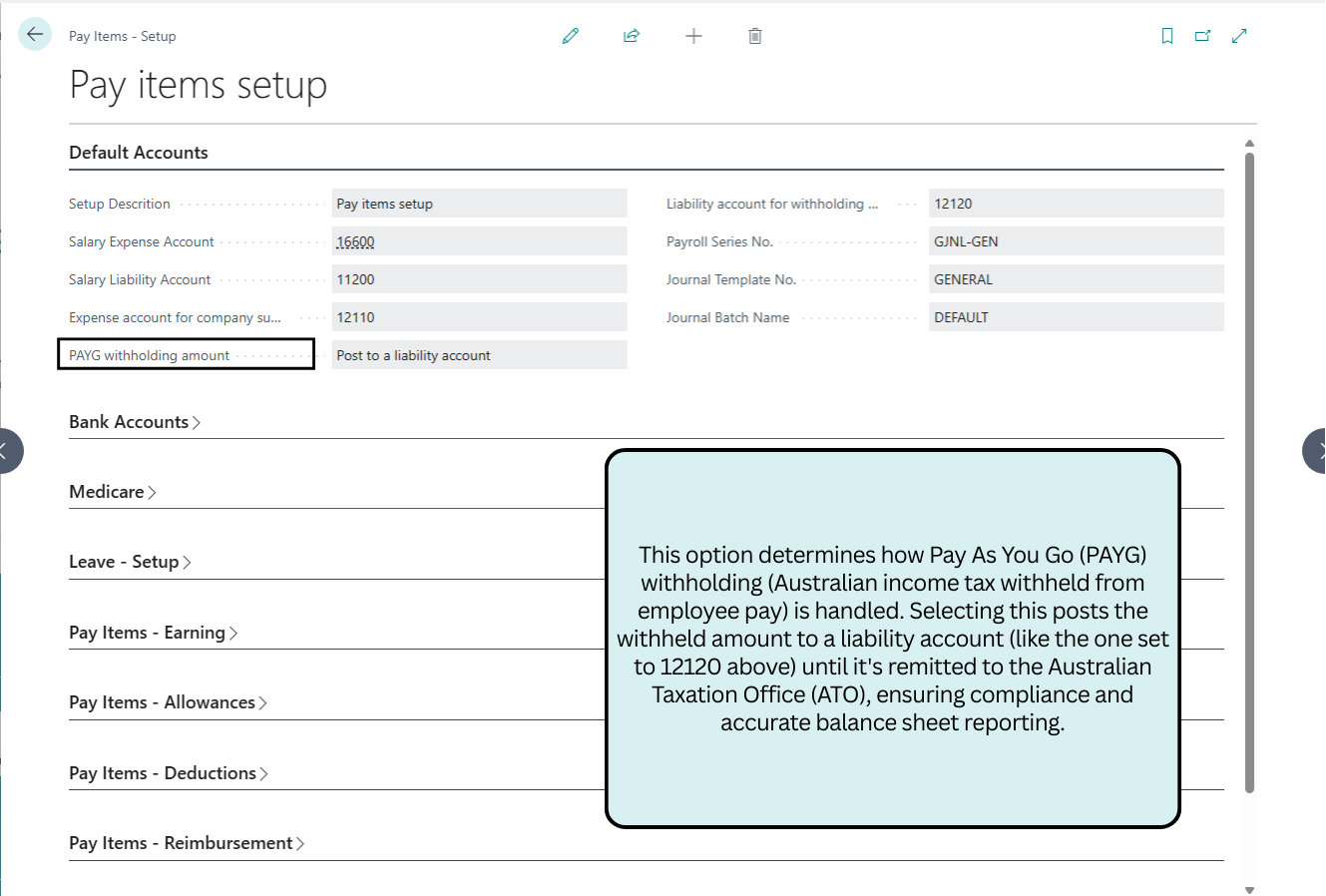
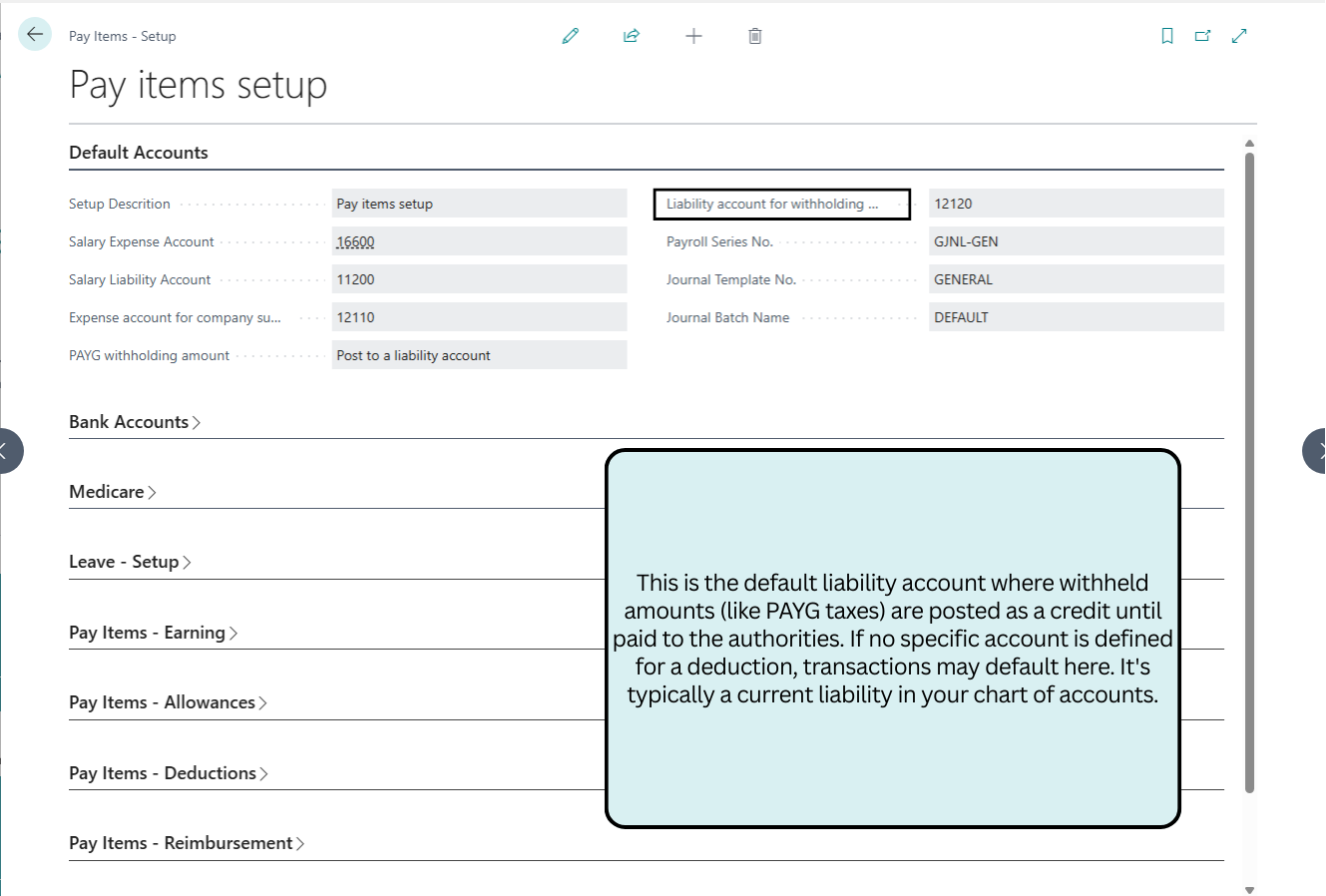
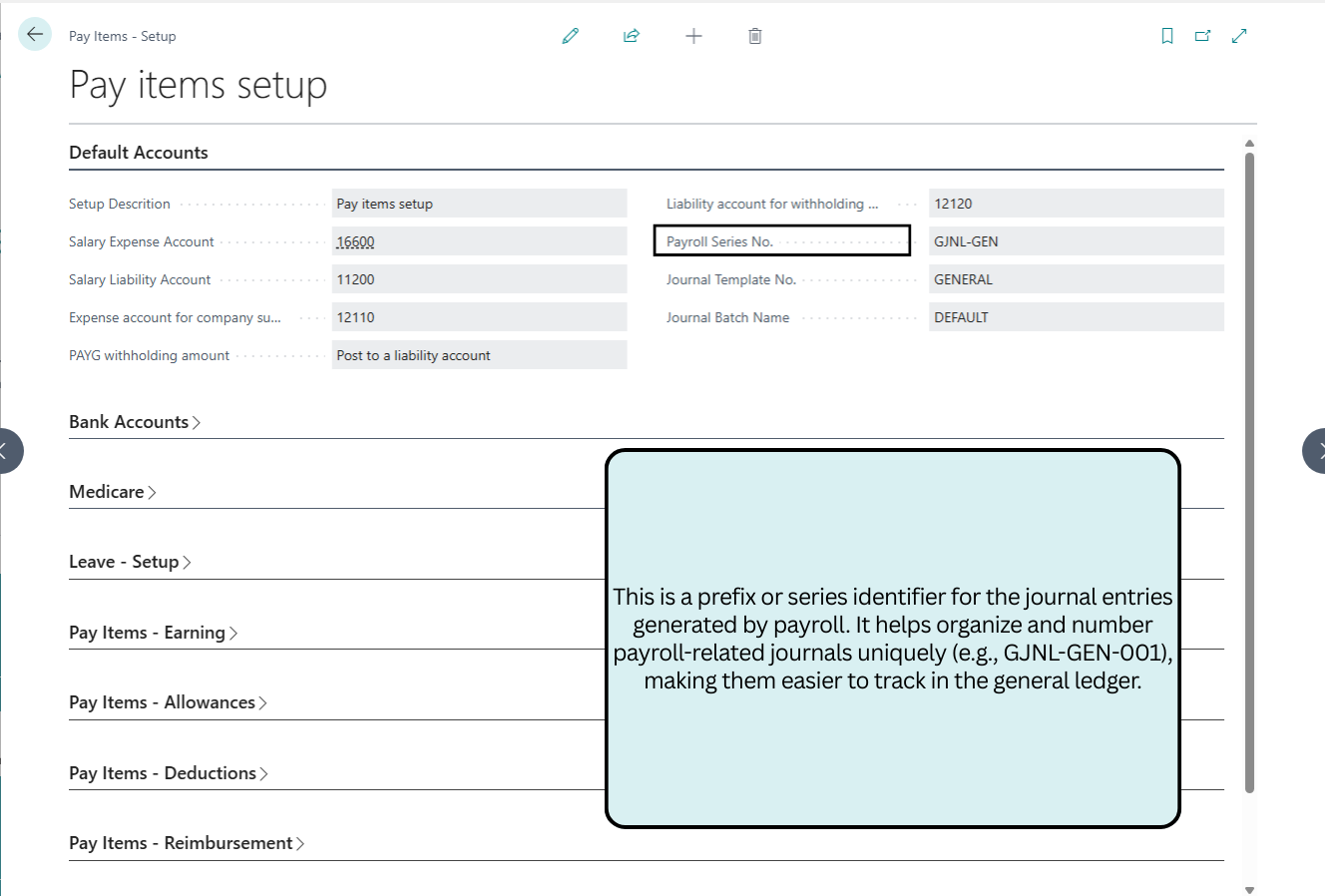
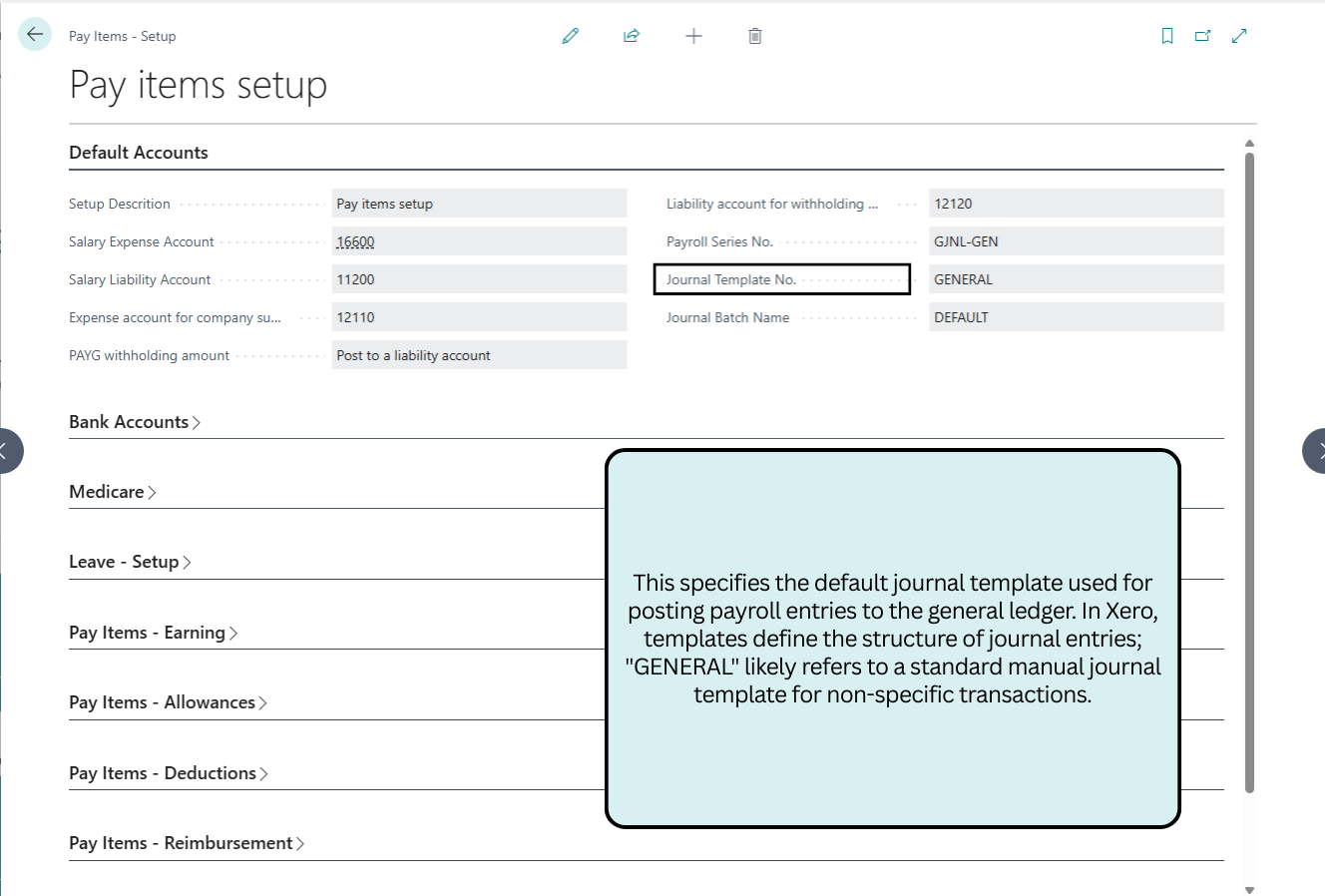
Default Accounts
This section configures core GL accounts for salary expenses, liabilities, superannuation, and PAYG withholding, ensuring accurate journal postings and ATO compliance.
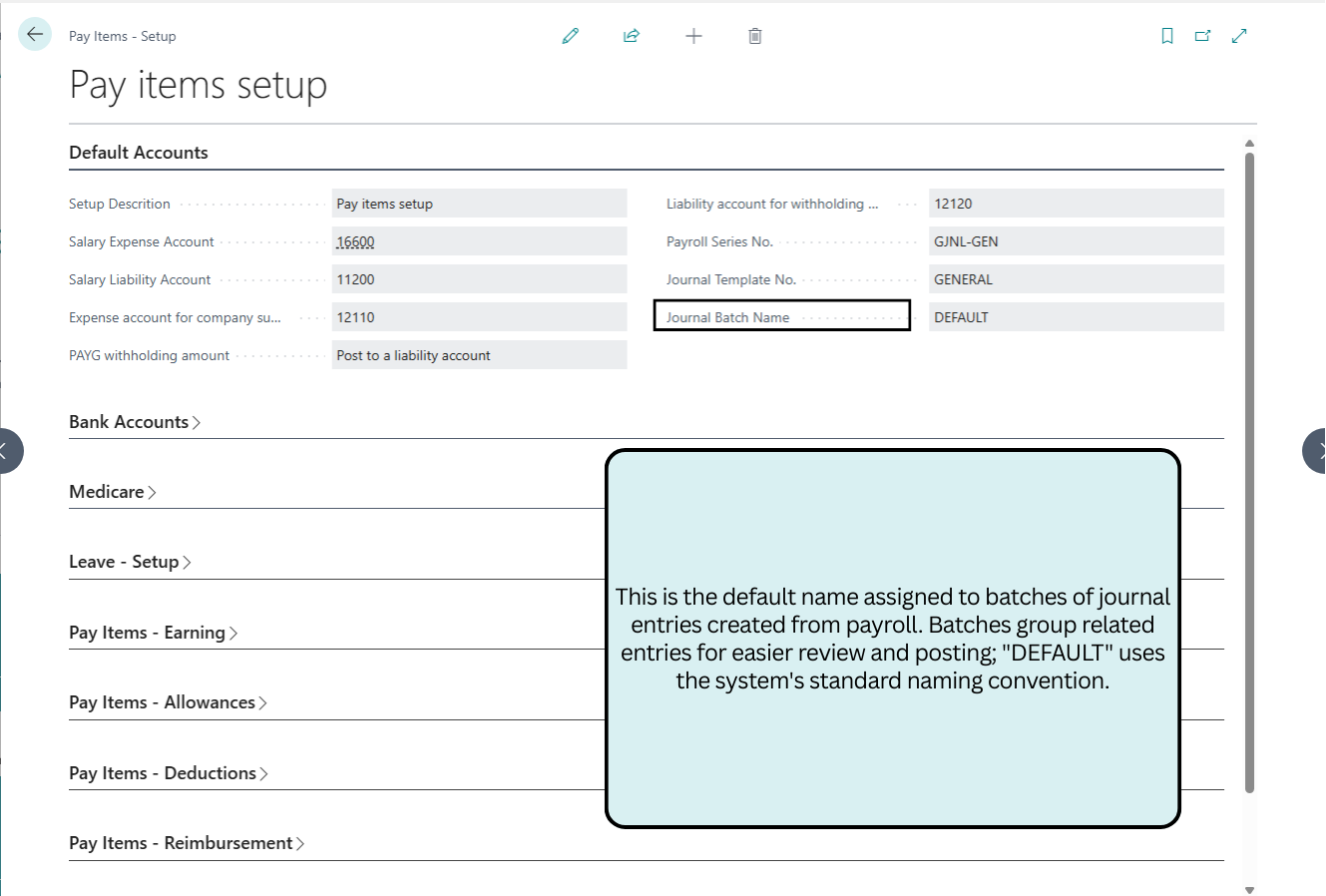
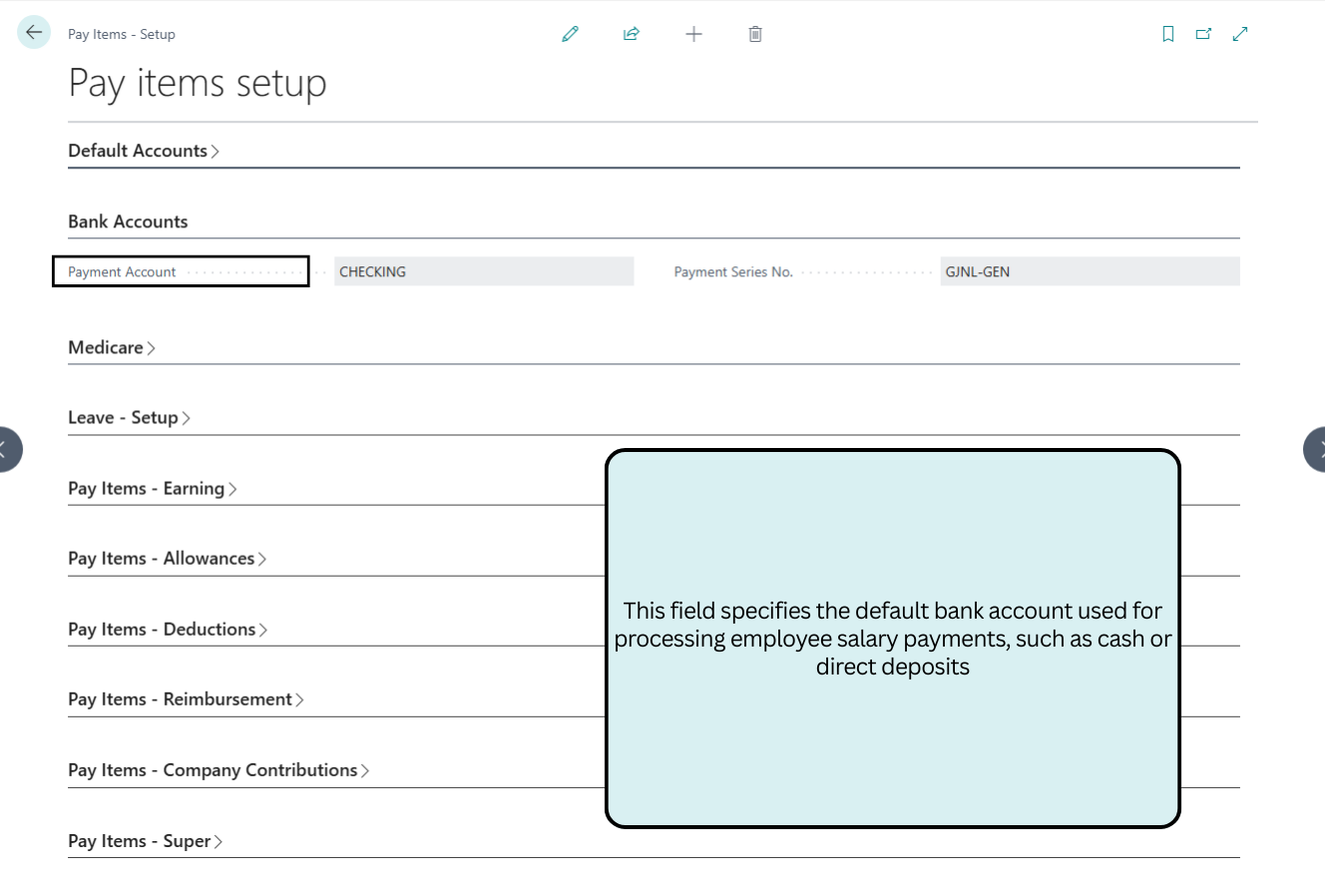
Bank Accounts
This manages configurations for employee payment processing, including the default bank account for disbursements and numbering series for payment journals.
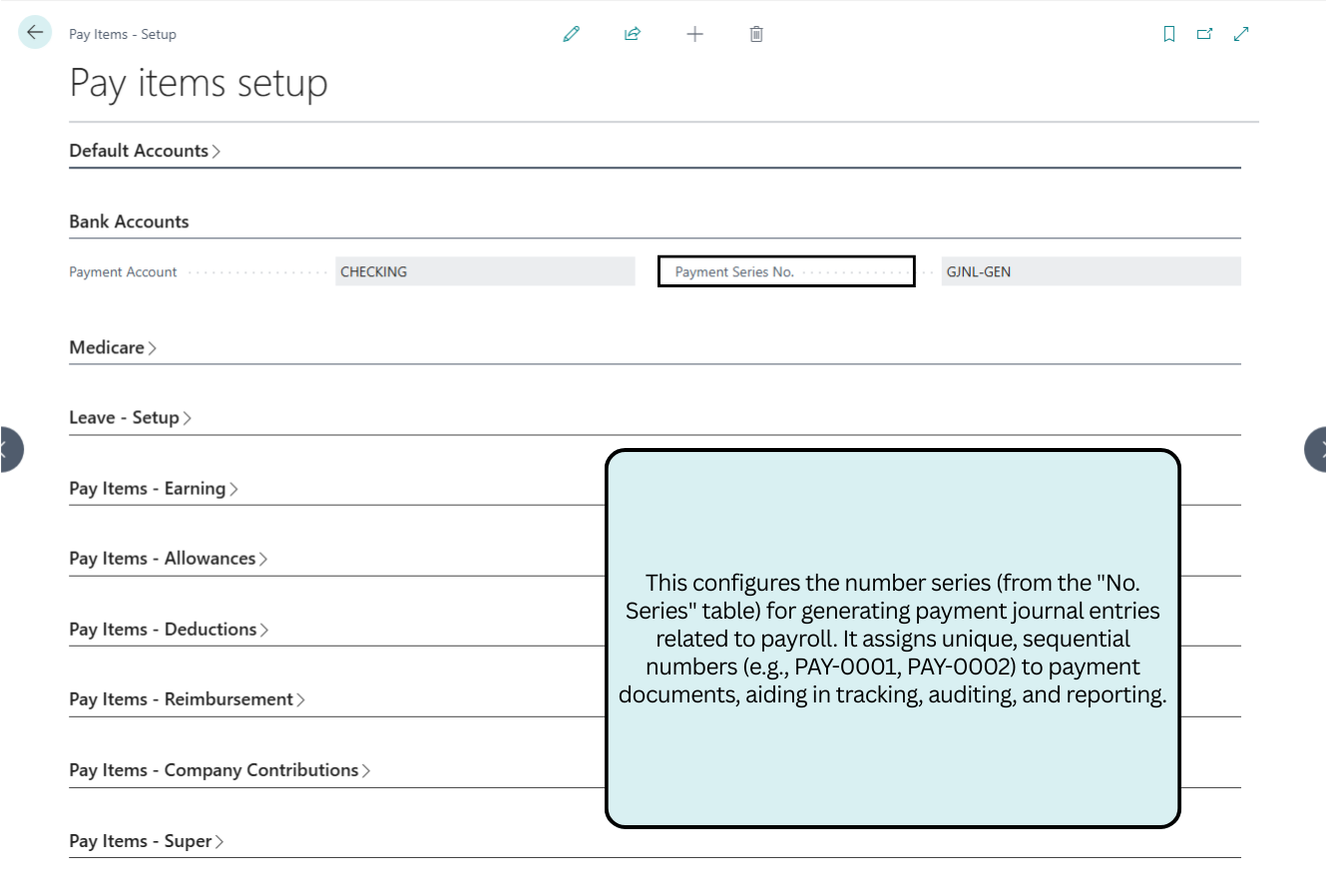
Medicare
Configures the default tax rates required for Australian healthcare compliance.
Leave Setup
This section defines how various leave types are accrued and processed for your employees.
| No. | Field Label | Description | Data Type |
| 1 | Leave Type | Choose from options like Annual, Long Service, Personal, or Other. | Options |
| 2 | Name | Assign a custom name to the leave type (e.g., “Annual Leave”). | Text |
| 3 | G/L Account | Select a specific G/L account for separate leave payment tracking; leave blank if not required. | Code |
| 4 | Annual Entitlement | Define the total hours an employee is eligible for annually. | Decimal |
| 5 | Accrual Period | Set the accrual frequency: Per Pay, Per Time Worked, or Per Annum. | Options |
| 6 | Maximum | Specify the maximum number of hours that can be accrued. | Decimal |
| 7 | Leave Loading | Define the percentage for leave loading and carry-forward rules. | Decimal |
| 8 | Status | Toggle to Active or Inactive. Inactive leaves will not appear for new employees. | Boolean |
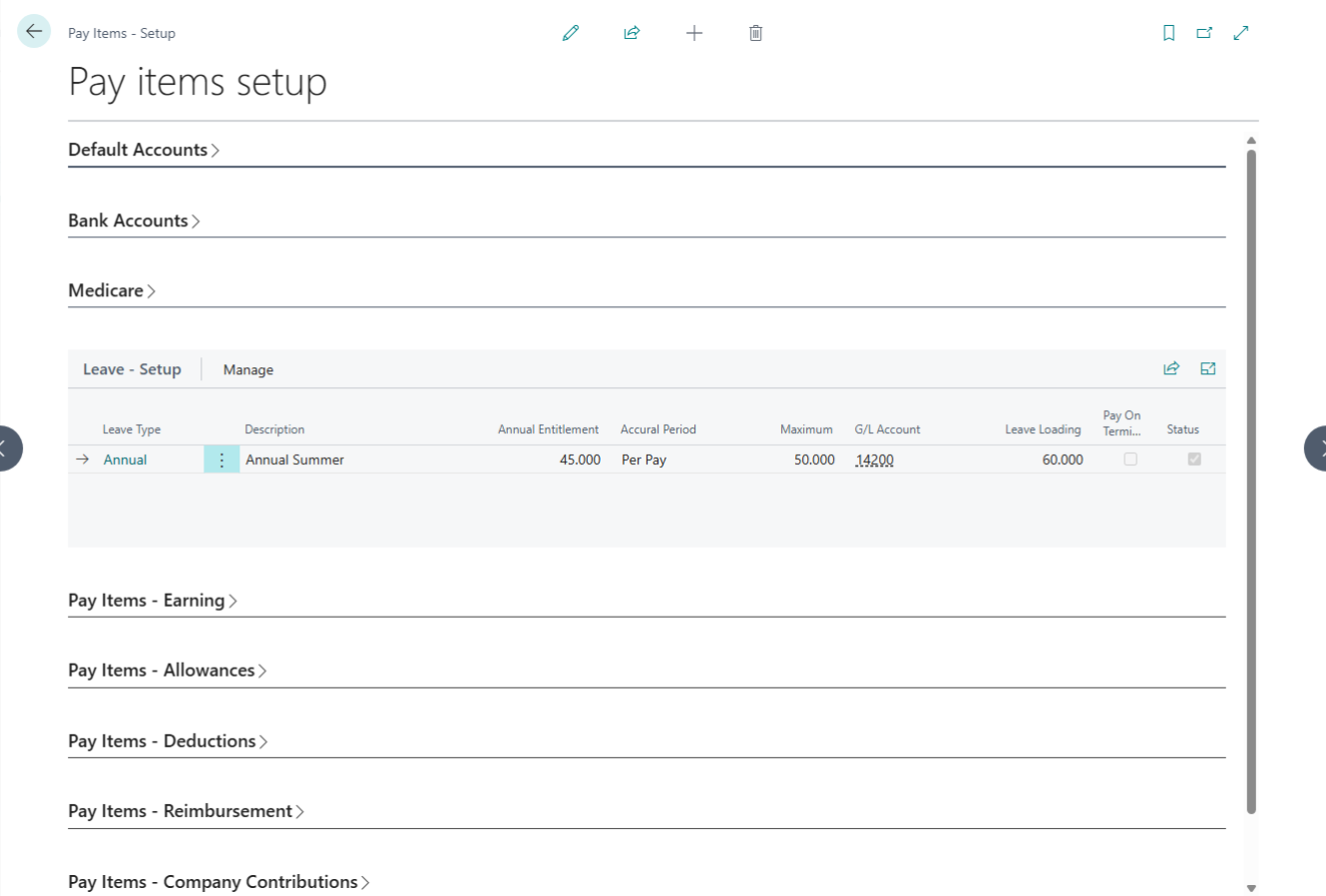
Earning Setup
To setup payroll extension all pay items need to be set proper. Especially Earning pay items are very important. Earning Pay items are all those items which will reflect employees earning.
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only label identifying the specific pay item category. | — |
| 2 | Sub Type | Select OTE, Overtime, Variable, or Terminate. This selection adjusts available sub-fields. | — |
| 3 | Description | The display name for the earning (e.g., “Monthly Salary”). Cannot be blank. | — |
| 4 | Pay Rate Basis | Defines the calculation method. SALARY is the recommended default. | — |
| 5 | G/L Account | Assign a specific expense account; otherwise, system defaults are used. | Chart of Accounts |
| 6 | Accrual Period | Coming Soon: Option to link earnings directly to leave accrual cycles. | — |
| 7 | Tax Applicable | Sets the tax treatment. Recommended: Gross Payment or No Tax. | — |
| 8 | Status | Toggle Active or Inactive. Inactive items are hidden from new employee setups. | — |
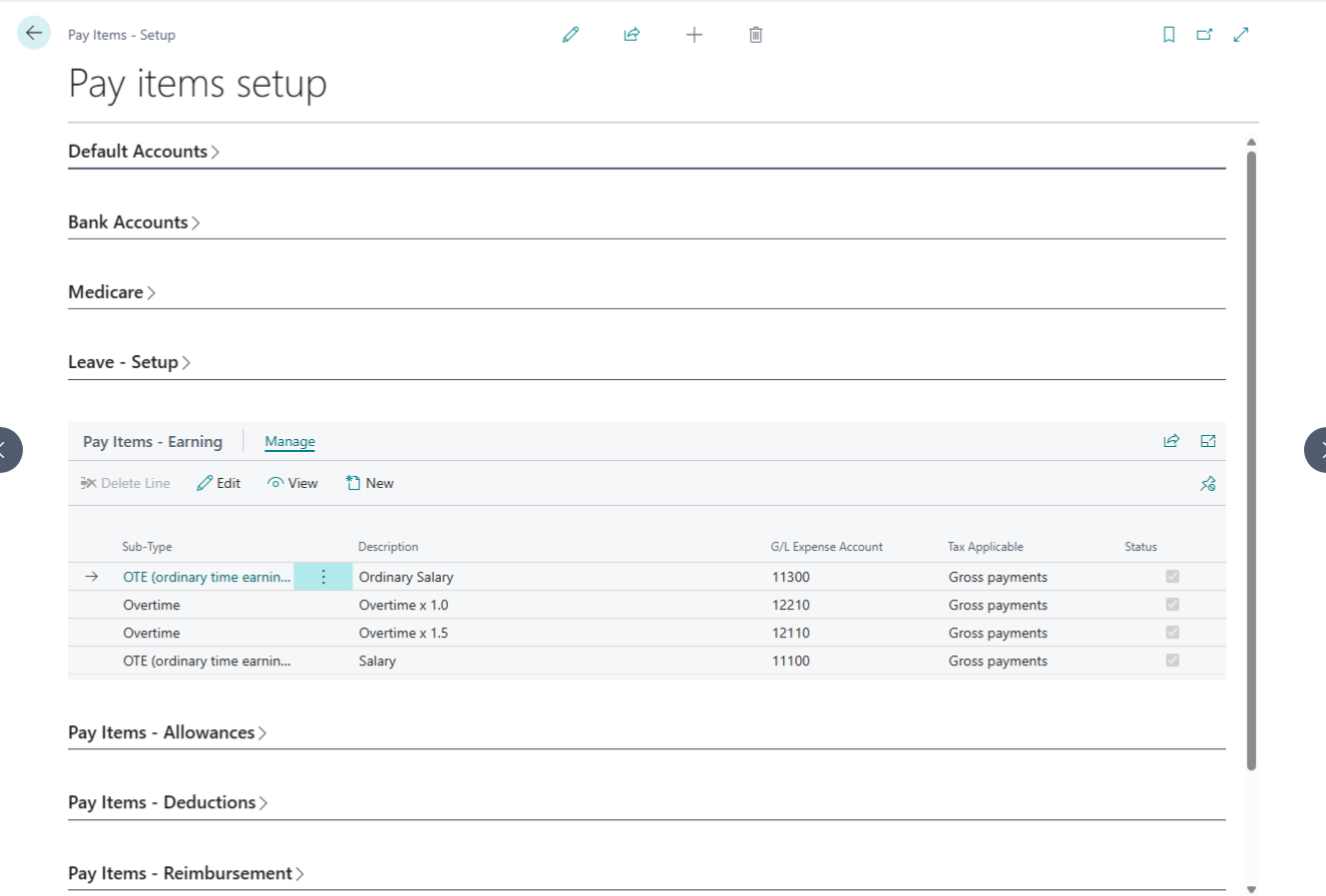
Allowance Setup
Allowances are also earning type but in the payroll system they are treated separately.
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only field indicating the specific category of the pay item. | — |
| 2 | Sub Type | Choose from Car, Travel, Meal, House, Transport, Laundry, or Others. Your choice determines which fields are active. | — |
| 3 | Description | The name of the allowance (e.g., “Lunch Allowance”). This field is required. | — |
| 4 | G/L Account | Map to a specific expense account or leave blank to use the system default. | Chart of Accounts |
| 5 | Calculation Basis | Select how the allowance is calculated: Quantity, Hourly, or Others. | — |
| 6 | Default Rate | Set a fixed rate for the allowance (e.g., $5.50 per unit). | — |
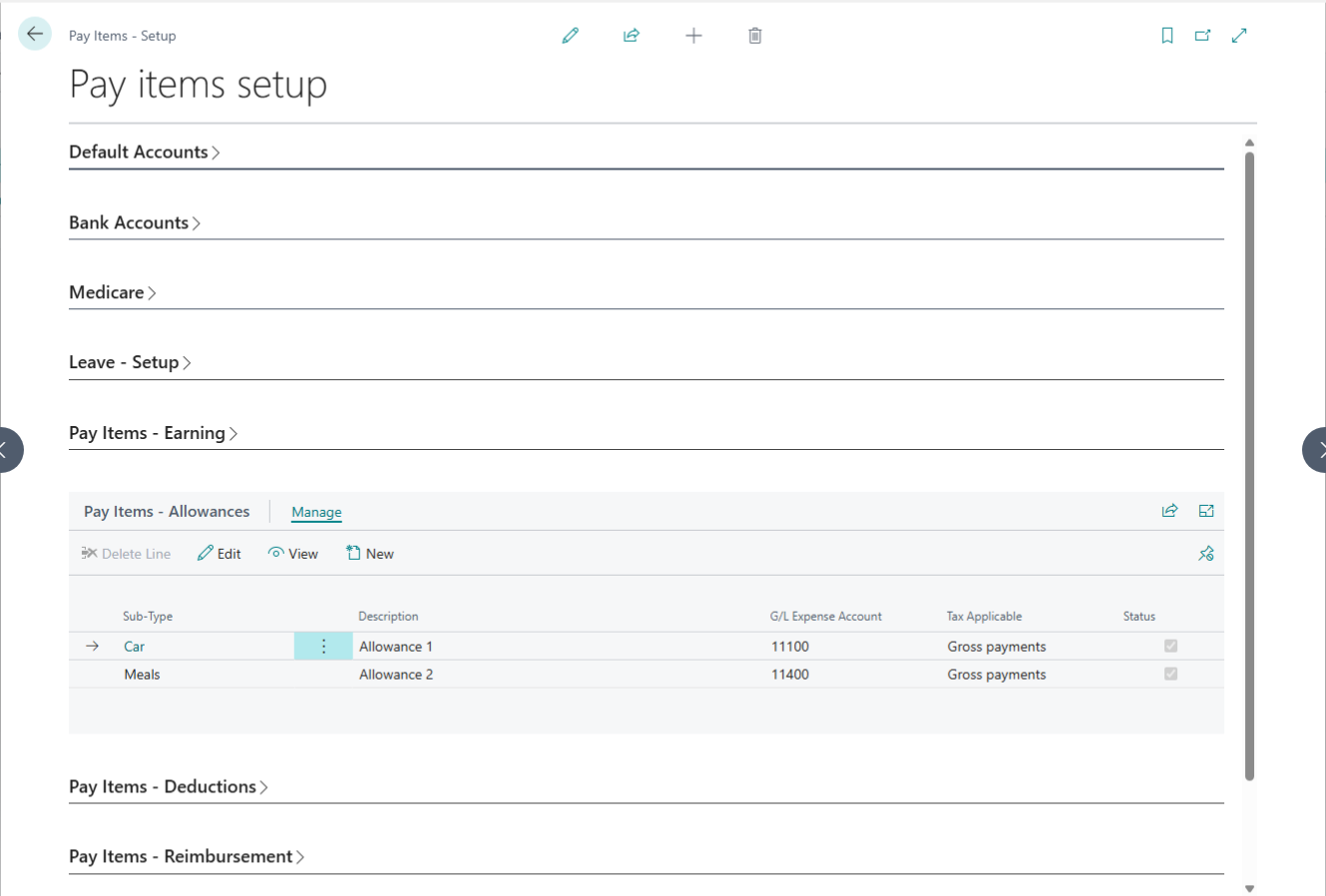
Deduction Setup
Deductions are those pay items which are deducted from Salary or earning.
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only label identifying the specific pay item category. | — |
| 2 | Sub Type | Choose from Professional Fee, Workplace Giving, Tax, or Others. Your choice determines active sub-fields. | — |
| 3 | Description | The name of the deduction (e.g., “PAYG”). This field is required. | — |
| 4 | G/L Account | Assign a specific liability account or leave blank to use system defaults. | Chart of Accounts |
| 5 | Payee | Link the deduction to a specific vendor for payment processing. | Vendors |
| 6 | Calculation Basis | Select the calculation method: Quantity, Hourly, or Others. | — |
| 7 | Deduction From Gross | Toggle True to deduct from gross salary; otherwise, it will deduct from net salary. | — |
| 8 | Default Rate | Set a fixed deduction amount (e.g., $10.00). | — |
| 9 | Limit | Set a maximum threshold or cap for the deduction (e.g., 12 occurrences). | — |
| 10 | Limited By | Define the limit frequency: Per Pay or Per Annum. | — |
| 11 | Status | Toggle Active or Inactive. Inactive items are hidden from new employee setups. | — |
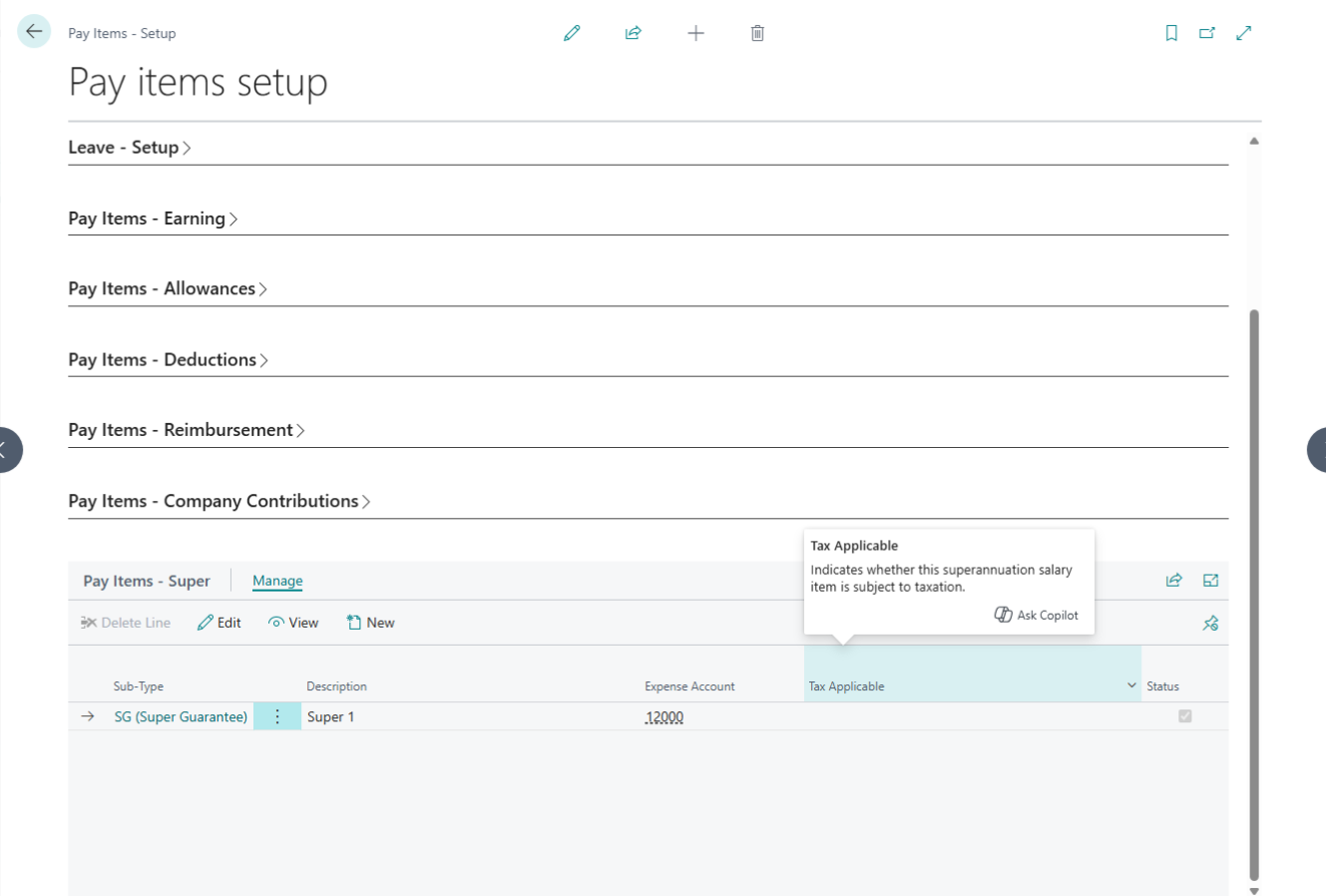
Reimbursement Setup
Configure employee reimbursement items for business expenses such as travel, meals, or training. Define rules for approval and payment processing.
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only label identifying the specific category of the pay item. | — |
| 2 | Description | The name of the reimbursement (e.g., “Travel Expense”). This field is required. | — |
| 3 | G/L Account | Assign a specific expense account or leave blank to use system defaults. | Chart of Accounts |
| 4 | Status | Toggle Active or Inactive. Inactive items are hidden from new employee setups. | — |
| 5 | Super Include | A sub-page view to manage how this item interacts with superannuation. | Super Sub-page |
| 6 | Super Item List | Access a comprehensive list of all defined superannuation pay items. | Super – Pay Items |
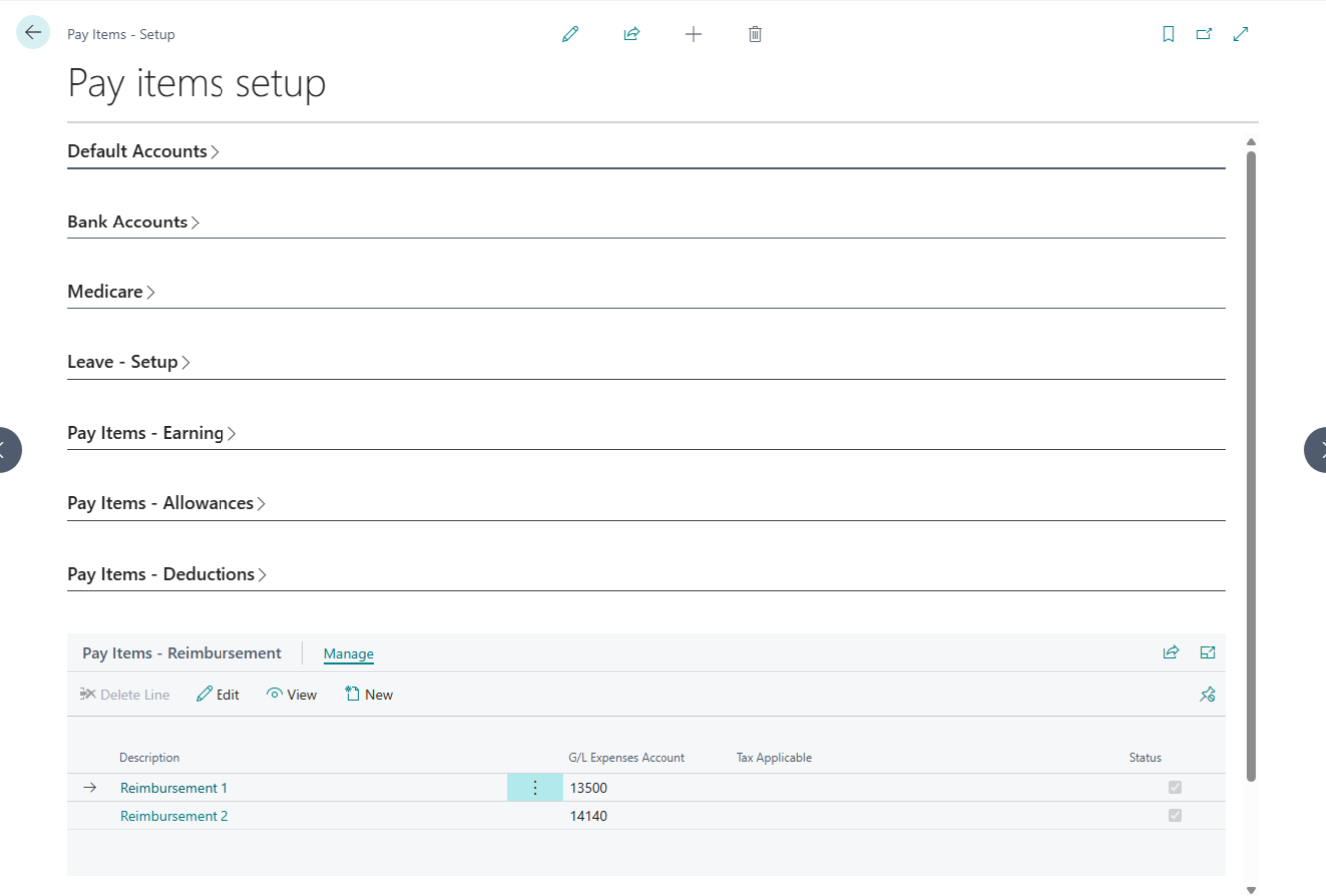
Company Contribution Setup
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only label indicating the specific category of the super item. | — |
| 2 | Description | The name of the super item (e.g., “Super Guarantee”). This field is required. | — |
| 3 | G/L Liability Account | Assign a specific liability account or leave blank to use system defaults. | Chart of Accounts |
| 4 | G/L Expense Account | Assign a specific expense account or leave blank to use system defaults. | Chart of Accounts |
| 5 | Payee | Link the super item to a specific vendor (Super Fund) for payment processing. | Vendors |
| 6 | Calculation Basis | Select how the amount is calculated: Quantity, Hourly, or Others. | — |
| 7 | Default Rate | Set a fixed rate for the super item (e.g., a specific dollar amount). | — |
| 8 | Limit | Define a maximum threshold or cap for this super item. | — |
| 9 | Limited By | Set the frequency for the limit: Per Pay or Per Annum. | — |
| 10 | Status | Toggle Active or Inactive. Inactive items are hidden from new employee setups. | — |
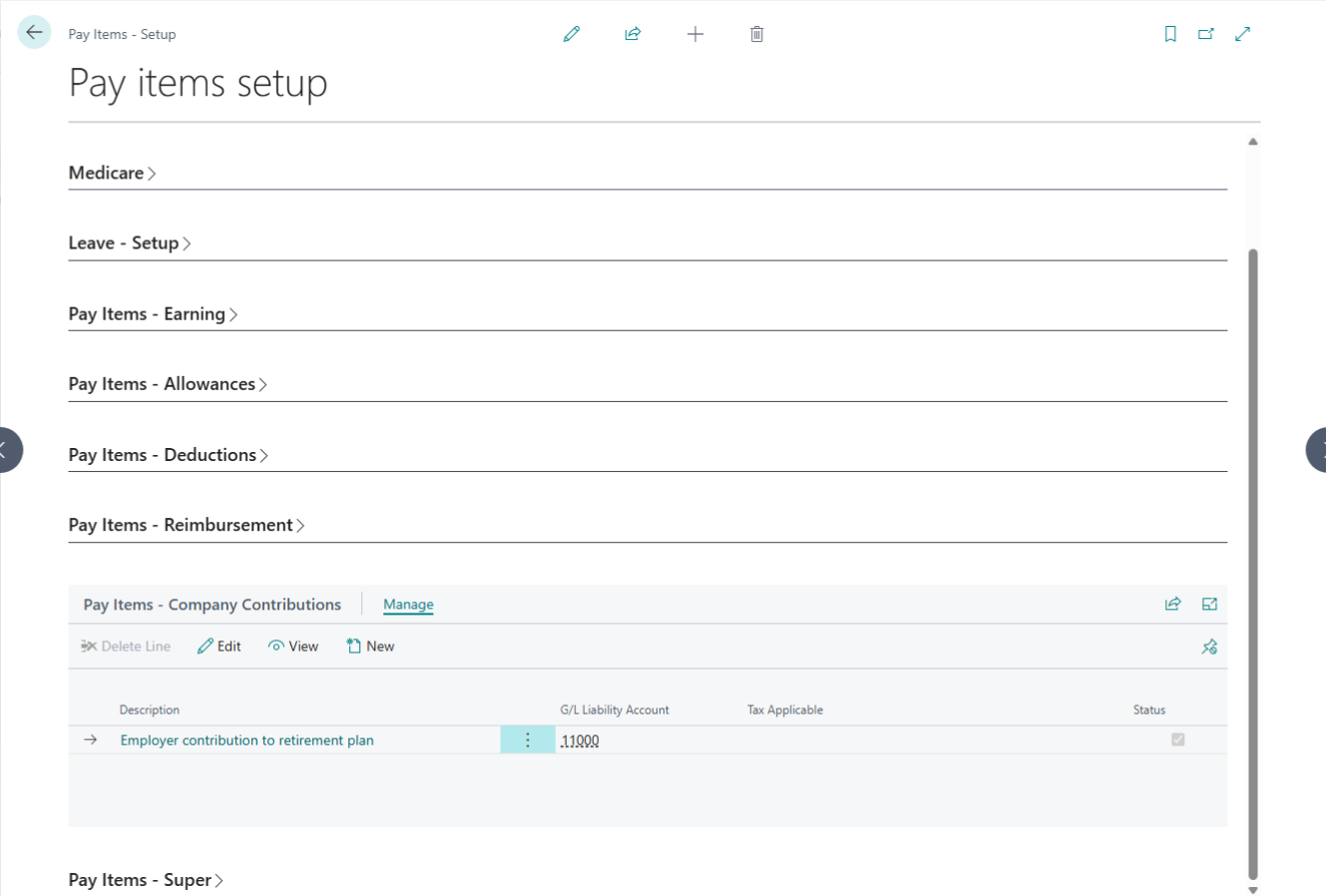
Superannuation Setup
| No. | Field Label | Description | Linked Page |
| 1 | Salary Item Type | A read-only label that identifies the type of pay item being added. | — |
| 2 | Sub Type | A dropdown including OTE, Overtime, Variable, or Terminate; your selection determines which other fields are active. | — |
| 3 | Description | The display name for the contribution (e.g., “Company Super”). This field cannot be blank. | — |
| 4 | G/L Expense Account | Define a specific expense account, or the system will use the default expense settings. | Chart of Accounts |
| 5 | Default Rate | Set the contribution rate as a percentage. | — |
| 6 | Use Statutory Rate | Toggle this on to automatically apply the current legal statutory rate. | — |
| 7 | Threshold Rate | Set the income threshold for contributions (default is $450). | — |
| 8 | Statutory Threshold | Toggle to apply the standard legal threshold requirements. | — |
| 9 | Maximum | Defines the maximum superannuation amount allowed for this item. | — |
| 10 | Limit | Set the maximum dollar limit for the contribution. | — |
| 11 | Limited By | Select whether the limit applies Per Pay period or Per Annum. | — |
Pay Runs
A Pay Run is the process of calculating and paying employee salaries for a specific pay period, such as weekly or monthly. It includes employee earnings, allowances, deductions, tax, superannuation, and net pay. Once a pay run is processed and posted, salary and payment records are securely stored and payslips can be generated.
Our Pay Run system guides you through each step; from creating a new pay run to paying employees—while ensuring accuracy, compliance, and full visibility of salary details.
How to create & post a Pay Run?
Managing Employee Pay Runs
A comprehensive guide to processing payroll, from initial setup to General Ledger posting and payslip distribution.
The Pay Run system is a guided, end-to-end workflow designed to handle employee earnings,
allowances, deductions, and tax compliance. By centralizing salary calculations and payment
records, the system ensures full visibility and financial accuracy for every pay period
System Features & Business Rules
- Compliance Guardrails: Prevents employees from being added to multiple open Pay Runs.
- Status Protection: Records are editable only in Draft status.
- Automated Tax Scaling: Defaults to Scale 2 but dynamically adjusts per employee tax setup.
- GL Integration: One-click posting keeps payroll and finance fully aligned.
- Bulk Actions: Post payments or download payslips for all employees at once.
Key Payroll Data Definitions
| Field Name | Description | Logic / Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Earning | Total pay before deductions | Earnings + Allowances |
| Taxable Income | Income subject to tax | Gross − Super (%) |
| Net Pay | Final amount paid to employee | Gross − Tax − Deductions |
| Superannuation | Employer retirement contribution | Calculated per period setup |
| Tax Scale | Applied tax table | Pulled from Employee Tax Setup |
Technical Troubleshooting
Why can’t I add an employee to a Pay Run?
The employee’s default salary cycle must match the Pay Run schedule, and the employee
must not already exist in another active, unposted Pay Run.
Why is the Modify action disabled?
For audit integrity, records can only be modified while the Pay Run is in
Draft status.
Can I change the payment date?
Yes. As long as the Pay Run is not marked as Paid, the Default Payment Date
can be updated
Salary Detail
| No. | Label | Description | Data Type | Linked Page |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pay Run Name | A schedule name representing multiple employees’ salaries. | Text | Pay Run |
| 2 | Pay Run Cycle | Defines how frequently employees are paid (weekly, monthly, etc.). | Option | Pay Run |
| 3 | Payment Date | The date on which salary payment is made. | Date | Pay Run |
| 4 | Current Status | Indicates whether the salary is in Draft, Posted, or Paid status. | Option | Pay Run |
| 5 | Employee No. | Unique reference number used to identify an employee. | Integer | Employee Card |
| 6 | Employee Name | Full name of the employee. | Text | Employee Card |
| 7 | Earnings | Base earnings amount used for tax calculations. | Decimal | Salary Detail |
| 8 | Allowances | Additional payments made on top of base earnings. | Decimal | Salary Detail |
| 9 | Gross Earning | Total income earned before any deductions. | Decimal | Calculated |
| 10 | Taxable Income | Income amount on which tax is calculated. | Decimal | Calculated |
| 11 | Tax | Tax withheld as per applicable tax scales. | Decimal | Calculated |
| 12 | Tax Offset | Reduces the total tax payable on taxable income. | Decimal | Tax Setup |
| 13 | Other Deduction | Additional deductions applied to the salary. | Decimal | Deductions |
| 14 | Super | Employer contribution deducted into the employee’s super account. | Decimal | Super Setup |
| 15 | Net Pay | Final amount paid after all deductions and tax. | Decimal | Calculated |
| 16 | Employee Salary Cycle | Defines the salary payment frequency for the employee. | Option | Employee Card |
| 17 | Tax Scales | Tax schedule used to calculate withholding amounts. | Integer | Tax Setup |
Salary Calculator
Managing payroll is more than just paying employees; it’s about precision, compliance, and transparency. For payroll administrators and HR professionals, calculating the fine details of PAYG tax, Medicare levies, and Superannuation can be a time-consuming manual task.
To solve this, we are excited to introduce the Salary Tax Calculator is a dedicated tool built directly into your Business Central environment to streamline salary modeling and tax accuracy.
Why Use the Salary Tax Calculator?
The Salary Tax Calculator is designed as a “what-if” and validation tool. Whether you are onboarding a new hire, planning annual raises, or double-checking a pay run, this card provides instant visibility into the financial breakdown of an employee’s package.
Dynamic Pay Cycles: Switch between Weekly, Fortnightly, and Monthly views to see exactly how cash flow is affected.
Comprehensive Tax Scaling: Select specific Tax Coefficient Scales (e.g., Scale 2) to ensure the calculation aligns with the employee’s specific ATO tax declaration.
Superannuation Integration: Toggle whether the gross income includes or excludes Superannuation with a single click.
Medicare Levy Calculations: Automatically isolates the Medicare portion of the tax to provide a clearer picture of the tax breakdown.
How it Works: A 3-Step Process
The calculator is organized into two intuitive sections: General Input and Calculated Results.
Define the Gross Package
Enter the Annually Gross Income. The system immediately calculates the base weekly income. From here, you select the Salary Cycle and the appropriate Tax Coefficient Scale.
Configure Superannuation
Does the salary package include Super? By toggling the Includes Superannuation field, the calculator will “back-calculate” the taxable income if the super is inclusive, or add it on top if it is exclusive. You can also manually adjust the Superannuation % (defaulting to current standards like 10% or higher).
One-Click Calculation
By clicking the Calculate Tax action, the system runs its internal logic to provide:
Income Tax: The PAYG portion of the withholding.
Medicare Levy: The specific levy amount based on annual thresholds.
Net Payable Amount: The final “take-home” pay the employee will see in their bank account.
| No. | Label | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Calc. Salary | Calculates the given annual salary. | Action |
| 2 | Calc. Tax | Calculates the tax for the selected salary cycle. | Action |
| 3 | Calc. Annual Income | Calculates the annual income based on cycle salary. | Action |
| 4 | Gross Income | Annual income after deduction of tax. | Decimal |
| 5 | Salary Cycle | Defines the frequency of salary calculation (weekly, fortnightly, monthly). | Option |
| 6 | Calc. Salary/Cycle | Amount of salary corresponding to the selected cycle. | Decimal |
| 7 | Weekly Income | Displays salary on a weekly basis. | Decimal |
| 8 | Tax Coefficients / Scales | Tax coefficient selected from the list of available tax scales. | Option |
| 9 | Include Superannuation | Enable to deposit a specific amount in the employee’s super account. | Boolean |
| 10 | Superannuation % | Percentage of salary deposited into superannuation. | Decimal |
| 11 | Calc. Income Tax | Calculated tax amount from salary. | Decimal |
| 12 | Calc. Medicare | Medicare levy calculated as a percentage of taxable income. | Decimal |
| 13 | Total Calc. Tax | Sum of income tax and Medicare levy. | Decimal |
| 14 | Calc. Super | Superannuation amount calculated from salary. | Decimal |
| 15 | Taxable Income | Salary amount after super but before tax deductions. | Decimal |
| 16 | Net Payable Amount | Final salary amount after all taxes and deductions. | Decimal |
Setting Up ATO Tax Coefficients
While the Salary Tax Calculator provides the interface for daily use, the real “brain” of the system lies in the Tax Setup. To ensure every calculation aligns perfectly with Australian Taxation Office (ATO) standards, administrators must configure the Tax Coefficients and Medicare Levy parameters.
The Core: Tax Coefficients Management
The DTE APS Tax Coefficients page is the central repository for the mathematical formulas provided by the ATO. Instead of hard-coded values, our system uses a dynamic coefficient model.
- Floor & Ceiling Amounts: Define the specific income brackets for each tax scale.
- Variable A & B: These fields represent the ATO’s algebraic variables used to calculate withholding amounts (e.g., $y = ax – b$).
- Tax Scale Categorization: Easily organize coefficients by Scale No. (e.g., Scale 1 for no tax-free threshold, Scale 2 for residents with a tax-free threshold).
- Foreign Resident Toggle: A dedicated “Is Foreigner” flag ensures that the higher tax rates for non-residents are applied automatically when required.
- Pro Tip: Keep these records updated annually. When the ATO releases new tax tables (typically on July 1st), simply update the variables here to maintain system-wide accuracy without needing a code deployment.
Handling the Medicare Levy
The Medicare Levy is a critical component of Australian payroll that often fluctuates based on thresholds and individual circumstances. The Medicare Levy Parameters page allows for granular control over these calculations.
- Scale No.: Links the levy calculation to the appropriate tax scale.
- Parameters: Detailed descriptions of the specific levy rule being applied.
- Amount: The specific threshold or percentage value used to calculate the levy.
- Status Control: Use the “Active/Inactive” toggle to phase out old legislative parameters while keeping a historical record for previous financial years.
| No. | Label | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Scale No. | Represents the specific tax scale being applied. | Options |
| 2 | Parameters | ATO-provided parameters associated with the tax scale. | Options |
| 3 | Amount | The numeric value assigned to each parameter. | Decimal |
| 4 | Status | Indicates whether the scale parameter is currently applied. | Boolean |
Why This Architecture Matters?
By separating the Calculator from the Tax Coefficients, we provide a system that is:
- Transparent: You can see exactly which “Variable A” or “Tax Rate” resulted in the final deduction.
- Audit-Ready: Every tax scale used in a pay run can be traced back to the coefficients in this setup.
- Future-Proof: As tax laws change, your HR team can update values in the Tax Coefficients list directly in the Business Central client.
| No. | Label | Description | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coefficient ID | Auto-incremental number for each tax coefficient. | Integer |
| 2 | Scale No. | Represents the specific tax scale being applied. | Options |
| 3 | Floor Amount | Lowest amount for this tax coefficient range. | Decimal |
| 4 | Ceiling Amount | Highest amount for this tax coefficient range. | Decimal |
| 5 | Operations | Comparison operation: greater, less, or equal. | Options |
| 6 | Variable A | First variable used in tax calculation formulas. | Decimal |
| 7 | Variable B | Second variable used in tax calculation formulas. | Decimal |
| 8 | Tax Rate | Percentage of tax applied to salary within this coefficient range. | Decimal |
| 9 | Is Foreigner | Indicates if the employee is a foreign resident or local. | Boolean |
| 10 | Status | Indicates whether this tax coefficient is active. | Boolean |
